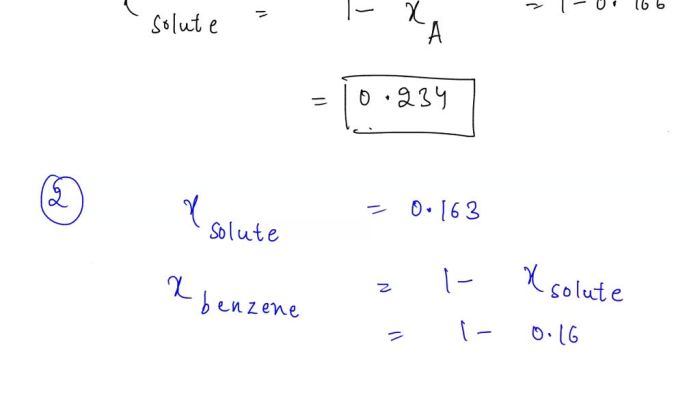Chemistry the molecular nature of matter and change 8th edition – Chemistry: The Molecular Nature of Matter and Change, 8th Edition, unveils the captivating world of chemistry, inviting readers to embark on an extraordinary journey into the fundamental principles that govern the behavior of matter and its transformations.
This comprehensive and engaging text provides a thorough exploration of the structure of matter, chemical reactions, energy, solutions, acids, bases, gases, nuclear chemistry, organic chemistry, and biochemistry, offering a deep understanding of the molecular nature of the world around us.
Key Concepts in Chemistry
Chemistry is the study of the composition, structure, properties, and change of matter. The fundamental principles of chemistry include the atomic theory, the law of conservation of mass, the law of definite proportions, and the periodic law. Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter and are composed of protons, neutrons, and electrons.
Molecules are formed when atoms combine, and ions are formed when atoms gain or lose electrons.
Role of Atoms, Molecules, and Ions in Chemical Reactions
Atoms, molecules, and ions interact through chemical reactions, which involve the rearrangement of atoms and the formation of new substances. Chemical reactions can be classified as synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, and combustion reactions.
Examples of Chemical Reactions and Their Applications
Chemical reactions have numerous applications in everyday life, including the production of food, medicine, and energy. Some examples of chemical reactions include the burning of fuels, the digestion of food, and the photosynthesis of plants.
Structure of Matter

Matter exists in three states: solid, liquid, and gas. Solids have a definite shape and volume, liquids have a definite volume but no definite shape, and gases have neither a definite shape nor a definite volume.
Relationship Between the Structure of Matter and Its Properties
The structure of matter determines its properties. For example, solids are generally hard and dense because their molecules are closely packed together. Liquids are generally less dense than solids because their molecules are more loosely packed. Gases are the least dense state of matter because their molecules are very far apart.
Role of Intermolecular Forces in Determining the Properties of Matter
The properties of matter are also influenced by intermolecular forces, which are the forces that act between molecules. Intermolecular forces can be strong or weak, and they can affect the melting point, boiling point, and viscosity of a substance.
Chemical Reactions: Chemistry The Molecular Nature Of Matter And Change 8th Edition
Chemical reactions are processes that involve the rearrangement of atoms and the formation of new substances. Chemical reactions can be classified as synthesis, decomposition, single displacement, double displacement, and combustion reactions.
Concepts of Stoichiometry and Equilibrium
Stoichiometry is the study of the quantitative relationships between the reactants and products in a chemical reaction. Equilibrium is a state in which the forward and reverse reactions of a chemical reaction occur at the same rate.
Factors That Affect the Rate of Chemical Reactions
The rate of a chemical reaction can be affected by several factors, including the concentration of the reactants, the temperature, the presence of a catalyst, and the surface area of the reactants.
Energy and Chemical Reactions

Energy is involved in all chemical reactions. Energy can be released or absorbed during a chemical reaction. Enthalpy is a measure of the heat content of a substance. Entropy is a measure of the disorder of a system. Free energy is a measure of the spontaneity of a chemical reaction.
Role of Energy in Chemical Reactions
Energy plays a crucial role in chemical reactions. Energy can be released or absorbed during a chemical reaction, and this energy can be used to drive other processes.
Concepts of Enthalpy, Entropy, and Free Energy
Enthalpy, entropy, and free energy are three important thermodynamic concepts that can be used to understand the energetics of chemical reactions.
Examples of Exothermic and Endothermic Reactions
Exothermic reactions release heat, while endothermic reactions absorb heat. Some examples of exothermic reactions include the burning of fuels and the digestion of food. Some examples of endothermic reactions include the melting of ice and the photosynthesis of plants.
Solutions and Their Properties

Solutions are mixtures of two or more substances that are uniformly mixed. The solvent is the substance that is present in the greatest amount, and the solute is the substance that is present in the lesser amount.
Components of Solutions, Chemistry the molecular nature of matter and change 8th edition
Solutions are composed of two main components: the solvent and the solute.
Types of Solutions and Their Properties
There are different types of solutions, including aqueous solutions, non-aqueous solutions, and solid solutions. Each type of solution has its own unique properties.
Factors That Affect the Solubility of Substances
The solubility of a substance is the maximum amount of that substance that can be dissolved in a given amount of solvent. The solubility of a substance is affected by several factors, including the temperature, the pressure, and the nature of the solvent and the solute.
FAQ Section
What are the fundamental principles of chemistry?
The fundamental principles of chemistry include the conservation of mass, the law of definite proportions, the law of multiple proportions, and the law of combining volumes.
What is the role of atoms, molecules, and ions in chemical reactions?
Atoms are the basic building blocks of matter, molecules are combinations of atoms, and ions are charged atoms or molecules. These particles interact with each other through chemical reactions, forming new substances with different properties.
What is the difference between exothermic and endothermic reactions?
Exothermic reactions release energy in the form of heat, while endothermic reactions absorb energy from the surroundings.