Which style of compressor uses belts to turn the compressor? Belt-driven compressors are a type of compressor that uses belts to turn the compressor. They are commonly used in a variety of industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and construction. Belt-driven compressors are known for their reliability, durability, and ease of maintenance.
In this article, we will discuss the working principle of belt-driven compressors, their advantages and disadvantages, and their applications. We will also provide a comparison of belt-driven compressors with other types of compressors.
1. Introduction

Compressors are essential components in various industries, providing compressed air for a wide range of applications. Among the different types of compressors, belt-driven compressors hold a significant position due to their versatility and adaptability. This article aims to provide a comprehensive overview of belt-driven compressors, exploring their working principles, applications, maintenance, and advancements.
2. Working Principle of Belt-Driven Compressors: Which Style Of Compressor Uses Belts To Turn The Compressor
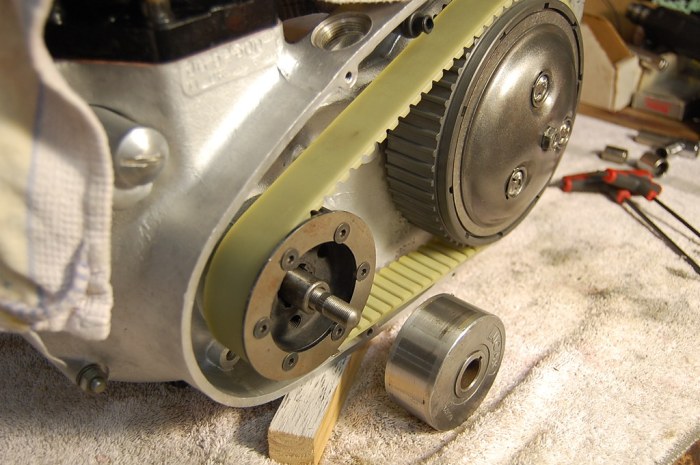
Belt-driven compressors utilize belts to transfer power from an electric motor or engine to the compressor’s crankshaft. The belt rotates the crankshaft, which in turn drives the pistons or impellers within the compressor. This mechanical arrangement allows for efficient power transmission and enables the compressor to generate compressed air.
Belt-driven compressors offer several advantages, including:
- Smooth and reliable operation due to the use of belts as a flexible power transmission medium.
- Reduced noise and vibration compared to direct-drive compressors.
- Easy maintenance and replacement of belts as they wear out.
However, belt-driven compressors also have some disadvantages:
- Potential for belt slippage, especially under heavy loads or extreme conditions.
- Regular belt maintenance and replacement can increase operating costs.
- Lower efficiency compared to direct-drive compressors due to power loss in the belt transmission.
There are different types of belt-driven compressors, including reciprocating, rotary screw, and centrifugal compressors. Each type has its own unique design and characteristics, catering to specific applications and performance requirements.
3. Applications of Belt-Driven Compressors

Belt-driven compressors find applications in a diverse range of industries, including:
- Automotive repair and maintenance shops for powering pneumatic tools and equipment.
- Manufacturing industries for operating machinery, painting, and cleaning.
- Construction sites for powering nail guns, drills, and other pneumatic tools.
- Food and beverage industry for packaging, conveying, and mixing operations.
- Medical and dental facilities for powering dental drills, surgical equipment, and respiratory devices.
When selecting a belt-driven compressor for a particular application, factors such as air flow rate, pressure requirements, duty cycle, and available power source should be considered. Proper sizing and selection ensure optimal performance and efficiency.
4. Maintenance and Troubleshooting of Belt-Driven Compressors
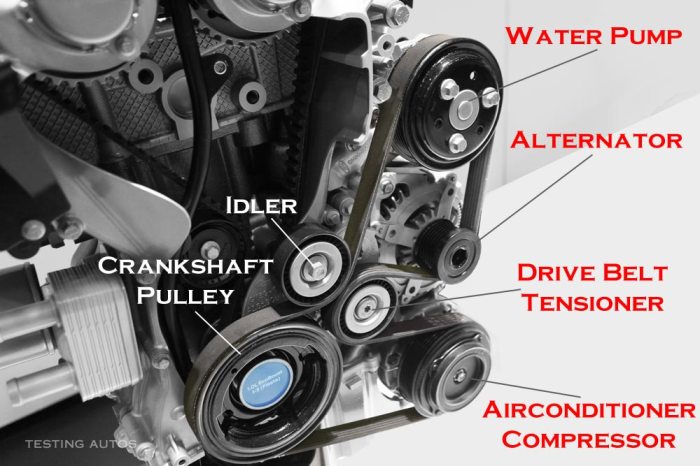
Regular maintenance is crucial for ensuring the longevity and reliability of belt-driven compressors. Recommended maintenance procedures include:
- Inspecting and replacing belts regularly to prevent slippage and premature failure.
- Checking and adjusting belt tension to ensure proper power transmission.
- Lubricating moving parts as per manufacturer’s recommendations.
- Cleaning air filters to prevent contamination and ensure efficient air intake.
- Monitoring air pressure and temperature to identify potential issues.
Common troubleshooting issues associated with belt-driven compressors include:
- Belt slippage: This can be caused by worn or loose belts, misalignment, or excessive load.
- Loss of air pressure: This can be due to leaks in the system, faulty valves, or insufficient air intake.
- Excessive noise or vibration: This can indicate belt problems, misalignment, or mechanical issues.
By promptly addressing these issues, downtime can be minimized, and the compressor’s performance can be maintained.
Key Questions Answered
What is a belt-driven compressor?
A belt-driven compressor is a type of compressor that uses belts to turn the compressor.
What are the advantages of belt-driven compressors?
Belt-driven compressors are known for their reliability, durability, and ease of maintenance.
What are the disadvantages of belt-driven compressors?
Belt-driven compressors are not as efficient as other types of compressors, and they can be noisy.
What are the applications of belt-driven compressors?
Belt-driven compressors are commonly used in a variety of industries, including manufacturing, automotive, and construction.